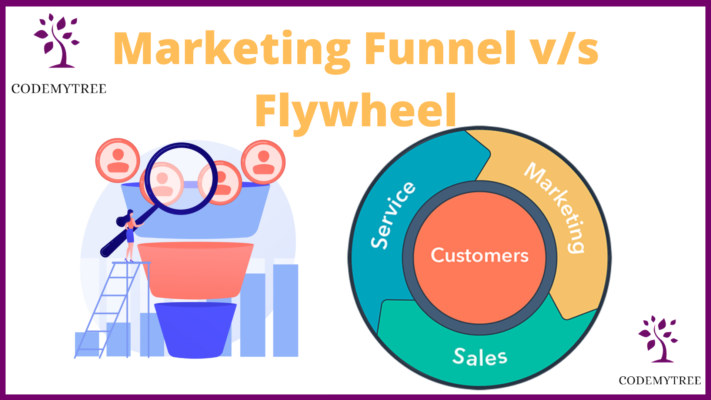
Developed in the late 1890s by Elias St.Elmo, the Marketing Funnel paved a way for marketers to understand their customer’s journey on a deeper level. But as time passed, the rise of inbound methodology helped developers discover a new concept named the Flywheel. It made its appearance in the inbound event 2018 and was introduced by Brian Halligan, the co-founder of HubSpot.
In this article, we will read about the following:-
- What is a marketing funnel?
- Why did it outdate?
- What is Flywheel?
- What made the transition from Marketing Funnel to Flywheel?
- Types of flywheel
- Flywheel v/s Marketing Funnel.
What Is Marketing Funnel?
It is a model which portrays the stages of a customer that is from the awareness stage to the purchasing stage. At the beginning of the funnel, the customer is recognized as the potential lead but by the end of the funnel they are referred to as loyal customers. There are four stages of the marketing funnel:
- Awareness stage
- Interest Stage
- Desire Stage
- Action Stage
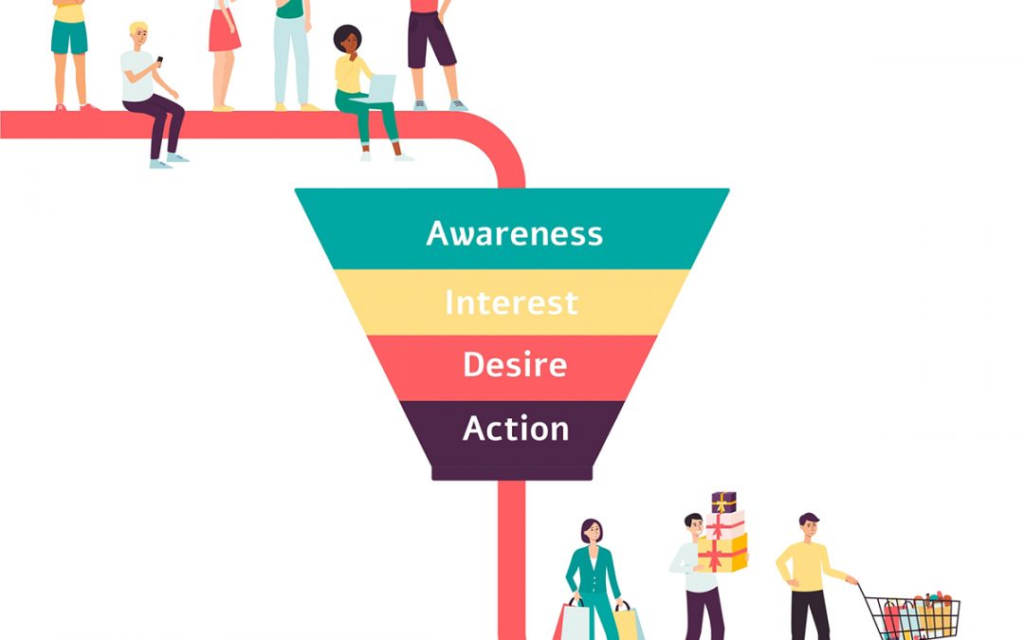
The initial number of potential leads doesn’t need to be equal to loyal customers. There are a lot of factors that affect the buyer’s journey which is why the entire model looks like a funnel.
Let’s look at the stages in detail.
1. Awareness Stage
This is the first stage aka the stage where the consumer’s journey begins, the potential lead comes to know about your product. There are various ways to create brand awareness, for instance:
- Publishing content in the form of blogs, newsletters, magazines etc
- E-mail marketing
- Social media marketing
- Organizing events and webinars
- Advertising in the form of PPC, display ads, etc
You can use the above marketing strategies to create brand awareness and visibility thereby beginning the buyer’s journey.
2. Interest Stage
Once the potential lead is aware of your product or services, it is necessary to tune their interest in your products and tell them how your products differ from the rest. For this, you will have to provide them with high-quality product content which will, in turn, convert them into qualified leads. This is your chance to build a strong relationship with the lead and push them into the next step, which is the Desire stage.

3. Consideration Stage
This stage gives you a rough sketch of the buyer’s journey, they could become a possible customer. To convince them into buying your product you will have to display offers through automated email campaigns and content revolving around products such as free demos, and FAQs to keep them interested because they are still potential leads and not converted customers.
4. Action Stage
Lastly, the action stage. This stage is also like the decision stage as the customer finalizes their decision that is whether or not they want to invest in your product. It is also the last stage of the marketing funnel. Usually, the action stage is subdivided into 3 additional stages:
- Intent: Analyze whether or not the lead is invested in the product and is planning to purchase it.
- Evaluation: Both sales and marketing team work together to effectively nurture the lead into purchasing the product
- Purchase: The last stage of the sub-stage is where the customers complete the purchasing process ad buys the product.
Using these stages, you can keep a track of your customer’s journey and nurture them through each stage so that they finalize the purchase.
According to Forbes, the funnel remained an integral part of marketing for about 122 years before the flywheel was developed and took away the power possessed by the marketing funnel. With time, the use of funnel diminished, and the flywheel was adopted.
Let’s look at the reasons why the use of the marketing funnel dropped over the years.
Why Did Marketing Funnel Lose It’s Stature?
As stated earlier, the marketing funnel remained in business for almost 122 years! But then what changed? For instance, Flywheel was introduced by HubSpot. HubSpot used a marketing funnel to grow into the huge industry they are today. What caused the need to develop a new marketing model?
Well, here are some reasons which justify just that:
1. Linear Strategy
Over time, the purchasing pattern of the customer journey has changed. Leads are no longer beginning their journey through the first stage, they could start it from anywhere. For instance, your search for a product gets a recommendation instantly, add it to the cart and purchase it. Over here you entered the consideration stage directly.
2. Treated customers as an afterthought
Another disadvantage of linear strategy is that it focuses on the customer only till the last purchasing stage, once that is attained the focus is shifted to another prospect. Imagine spending so much time and effort into converting only to start at square one again, that is tedious.
3. Major focus: customer attraction
When the marketing funnel originated, the information and medium through which information was scarce which are why it was easy to capture a customer’s attention. But in the modern era of technology, sales executives find it difficult to attain customer attraction.
Due to all these issues, Developers felt the need to introduce a model which catered to customers even after the purchase, wasn’t linear or cyclic, and had ways to attract customers. This is where Flywheel came into being.

Flywheel: The Innovation Which Changed The Marketing Dynamics.
Customers cannot be active promoters of your brand and attract more business if the funnel ignores one of the most significant aspects of the buyer’s experience today.
In contrast, the flywheel considers that customers can enter their journey at any point in the sales cycle. Some people may have already been able to purchase. A few people may have heard of your business and products. Still, some leads won’t know your brand.
Like any wheel, it spins in a circle continuously moving your customers through each phase of your inbound marketing strategy. As your flywheel accelerates, momentum builds and your business grows. What drives the wheel? Your customers’ delight and satisfaction. The more satisfied customers you have, the more sales you generate and the more satisfied customers you’ll have.
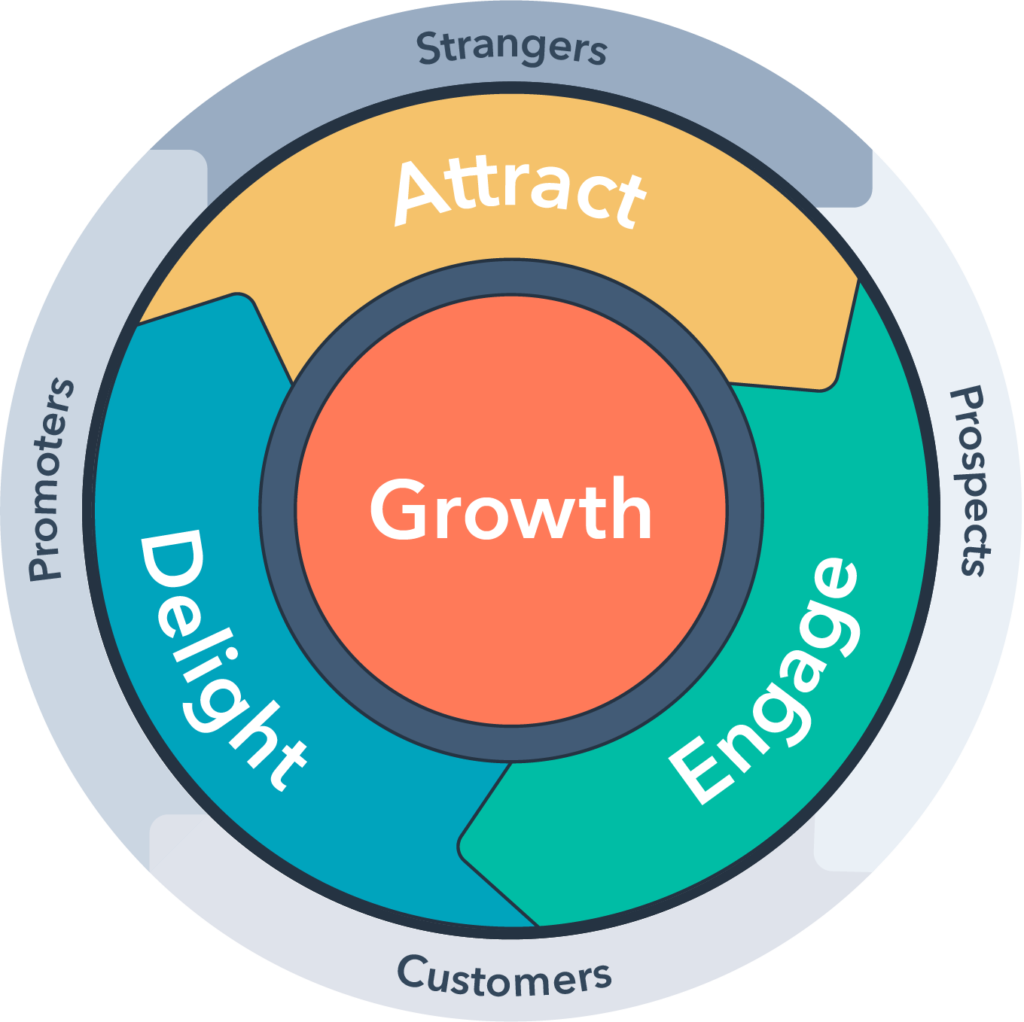
Types Of Flywheel
There are three types of flywheels following the same demographic. But the factors under each term differ let’s see how.
1. Marketing Flywheel
| Attract | Engage | Delight |
| blog posts & guides | Surveys | Smart content |
| social media marketing | Call-to-action | Follow up surveys |
| SEO optimizer | E-mail marketing | Performance monitoring |
| Offers | Chatbots and virtual assistance | |
| Case studies |
2. Sales Flywheel
| Attract | Engage | Delight |
| Analyzing prospects | Phone conversations | Sales enablement |
| Sequencing e-mail | Follow-up email | One-sheets |
| Link to calender | In-person meeting | Demo videos |
| Automating Sales | Case studies |
3. Service Flywheel
| Attract | Engage | Delight |
| Sales call | Strong support | Success stories |
| Performing assessment | 24/7 availability | Mobile Friendly rewards |
| Freemium offerings | ||
| Product demos |
Flywheel V/S Marketing Funnel
The flywheel methodology places customers at the center of the sales process, unlike the marketing funnel methodology which views them as an outcome or a means to an end. A business’s growth is enhanced by its active participation. Therefore, it is imperative to invest in improving the buyer’s experience. Take the HubSpot flywheel and watch your business grow exponentially if you’re still stuck in the funnel mentality.